The role of gut microbiota metabolism of lactate in the etiology of infant colic and digestive symptoms: Development of a trophic intervention with functional bacteria – Swiss National Science Foundation
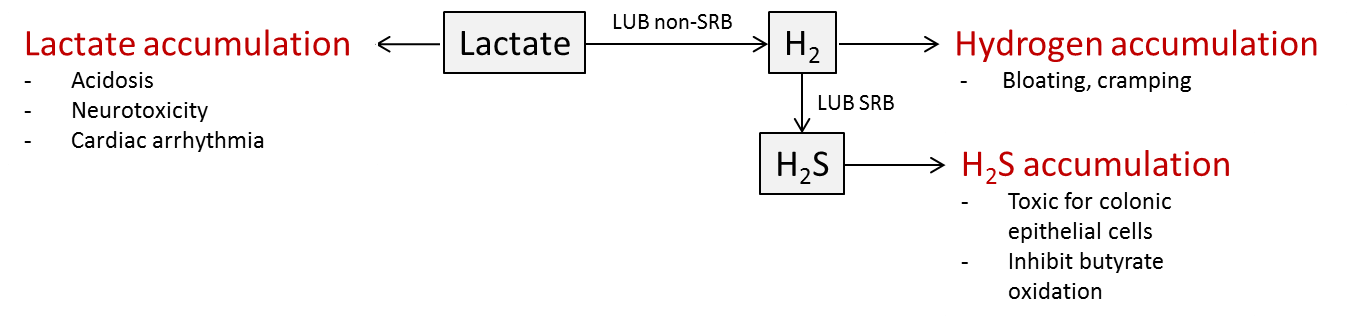
The human gut is the natural habitat for a large, diverse and dynamic bacterial community with important and specific functions which significantly impact the host health and disease, providing developmental, nutrition and protection effects. Lactate is produced by a number of bacteria and playing an important role in the trophic chain. Lactate is further completely metabolized by lactate-utilizing bacteria (LUB) in the healthy colon whereas it accumulates in certain gut disorders, with serious consequences such as neurotoxicity and cardiac arrhythmia during antibiotic treatment. In a recent project we showed that most of the primary colonizers of healthy infant gut are lactate-producing bacteria (LPB). Despite intensive investigation of the gut microbiota and its relation to infants’ health and disease over the past decades, the LUB community and sequence of colonization in the infant gut have never been studied. Furthermore the possible impact of the development of the trophic chain with LPB and LUB in the genesis of early and possibly lifelong diseases has never been investigated.
In this project we hypothesized that dysbiosis of the LUB followed by changes in the microbial metabolism may play a role in the etiology of early gastrointestinal discomforts in infants such as colic. Hence, early inoculation and colonization of LUB in the gut of infants may prevent such diseases. The general objective of this project is the functional characterization, enumeration and isolation of LUB in healthy infants from birth up to 2 years using a combination of cultural and state of the art molecular methods.